指针与地址
1. int * //声明指针 2. * //去引用 3. & //获取地址
Storing addresses in pointers
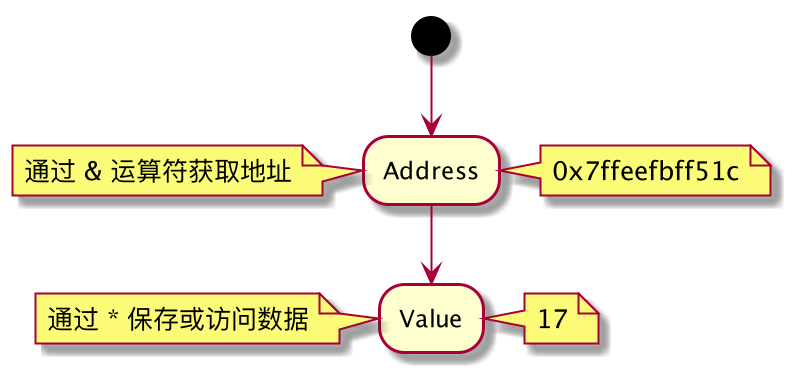
用int *可以声明一个指针类型变量。它不直接保存变量的数值,而是保存一个内存地址。
int i = 17;
int *addressOfI = &i;
printf("i stores its value at %p\n", addressOfI);
%p 是针对内存地址的格式说明符。
现在,我们知道了变量的地址也就可以得到其数值。如何得到呢?接着看。
Getting the data at an address
通过 * 运算符,我们可以访问保存在某个地址中的数据。
int i = 17;
int *addressOfI = &i;
printf("the int stored at addressOfI is %d\n", *addressOfI);
通过指针访问某个地址中数据这一过程,有时我们也称之为去引用。
Getting addresses
通过 & 运算符,我们可以获取变量的地址。
int i = 17;
printf("i stores its value at %p\n", &i);
Visual are more powerful than words
Comments:
Email questions, comments, and corrections to hi@smartisan.dev.
Submissions may appear publicly on this website, unless requested otherwise in your email.