算法通关40讲
算法/数据结构/系统设计
时间复杂度/空间复杂度
Big O notation O(1): Constant Complexity(常数复杂度) O(log n): Logarithmic Complexity(对数复杂度) O(n): Linear Complexity(线性时间复杂度) O(n^2): N square Complexity(平方) O(n^3): N square Complexity(立方) O(2^n): Exponential Growth(指数) O(n!): Factorial(阶乘)

Array & Linked List
Array
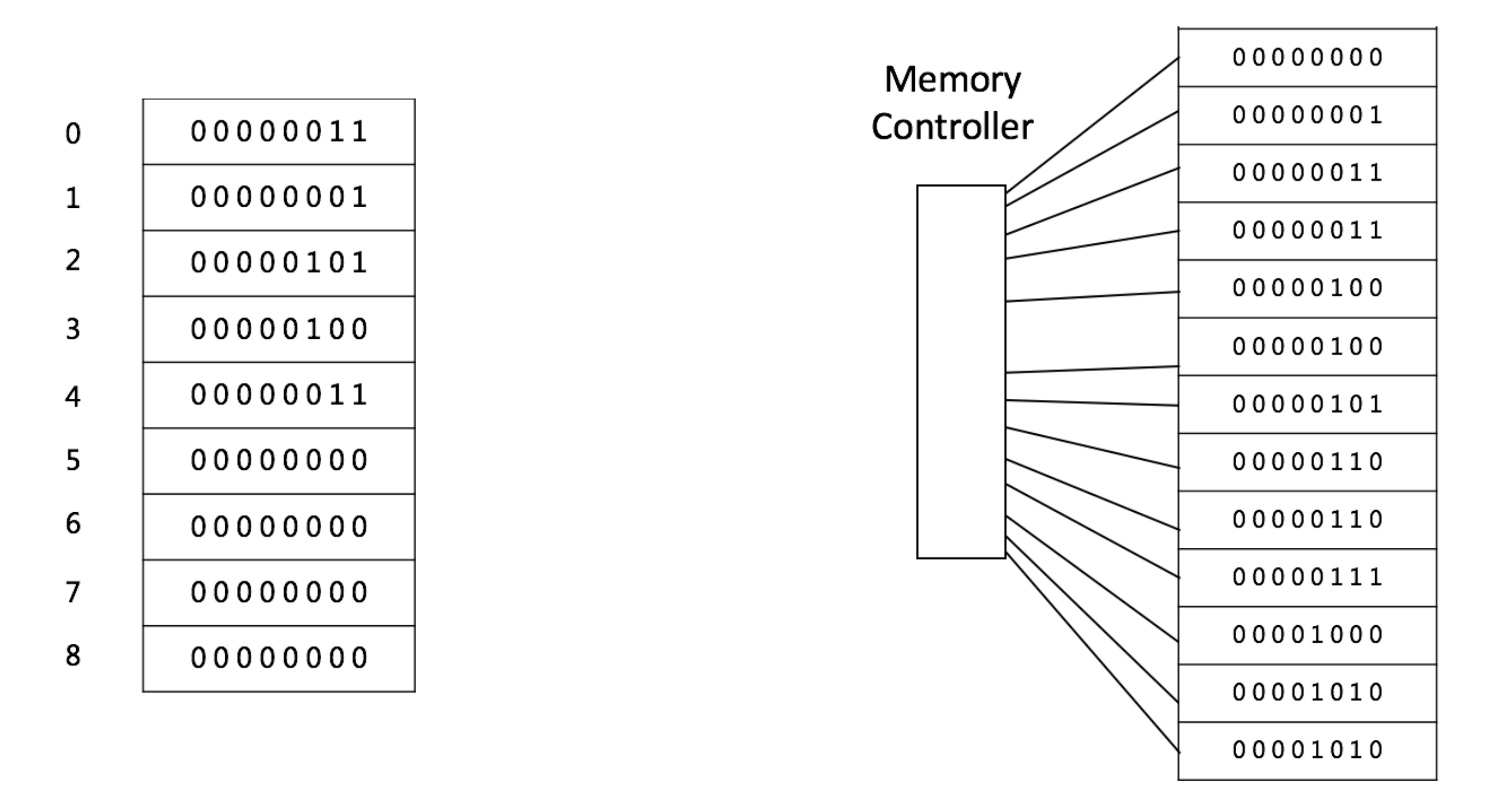
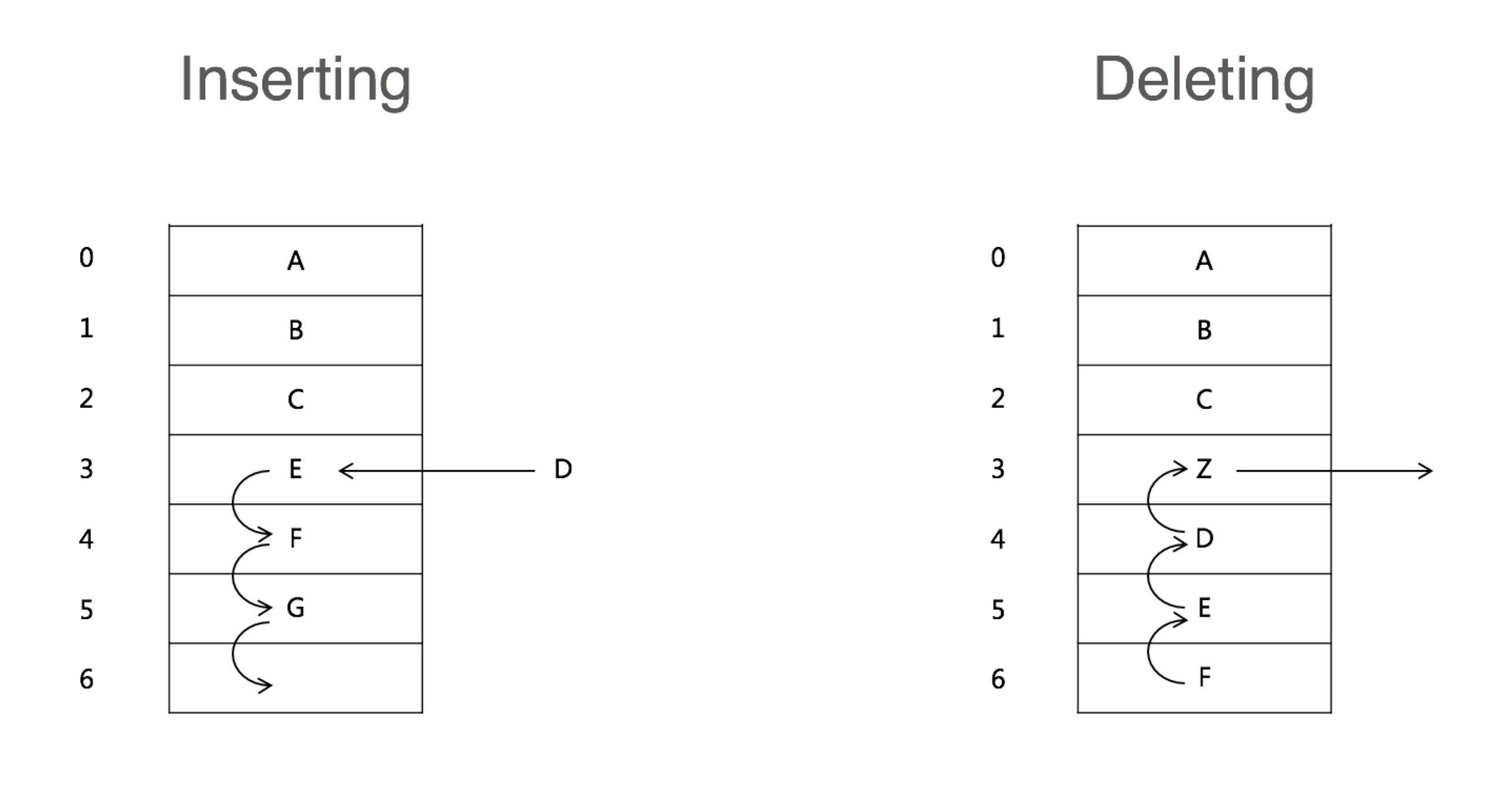
复杂度分析 Access: O(1) Insert: 平均O(n),如果插入到最后一个则是O(1) Delete: 平均O(n),如果删除最后一个则是O(1)
Linked List
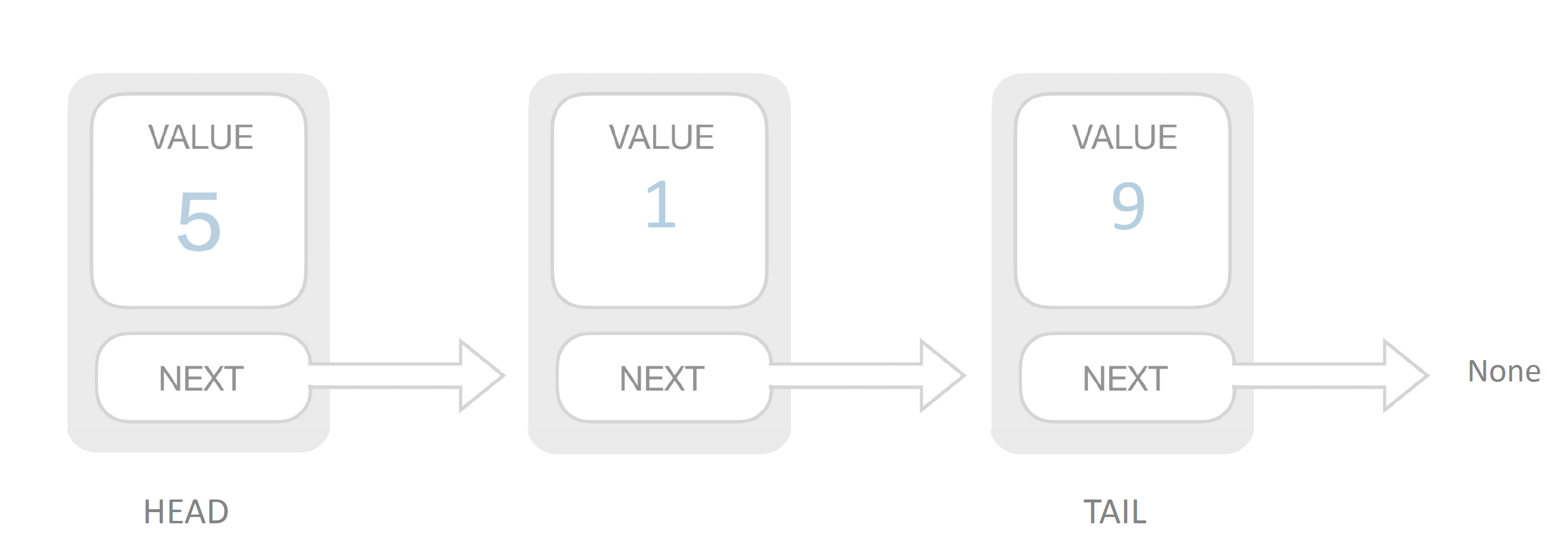
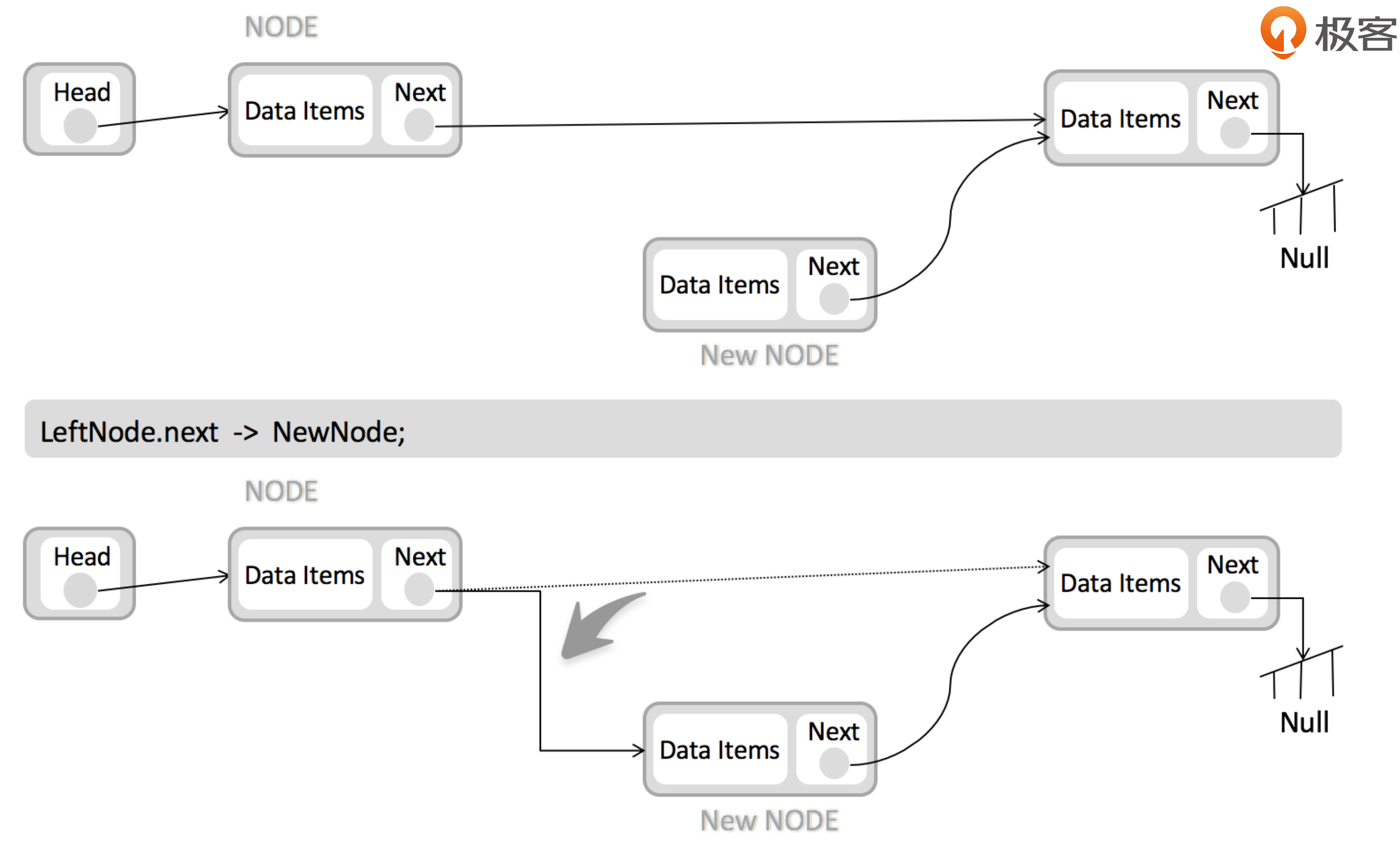

Doubly Linked List
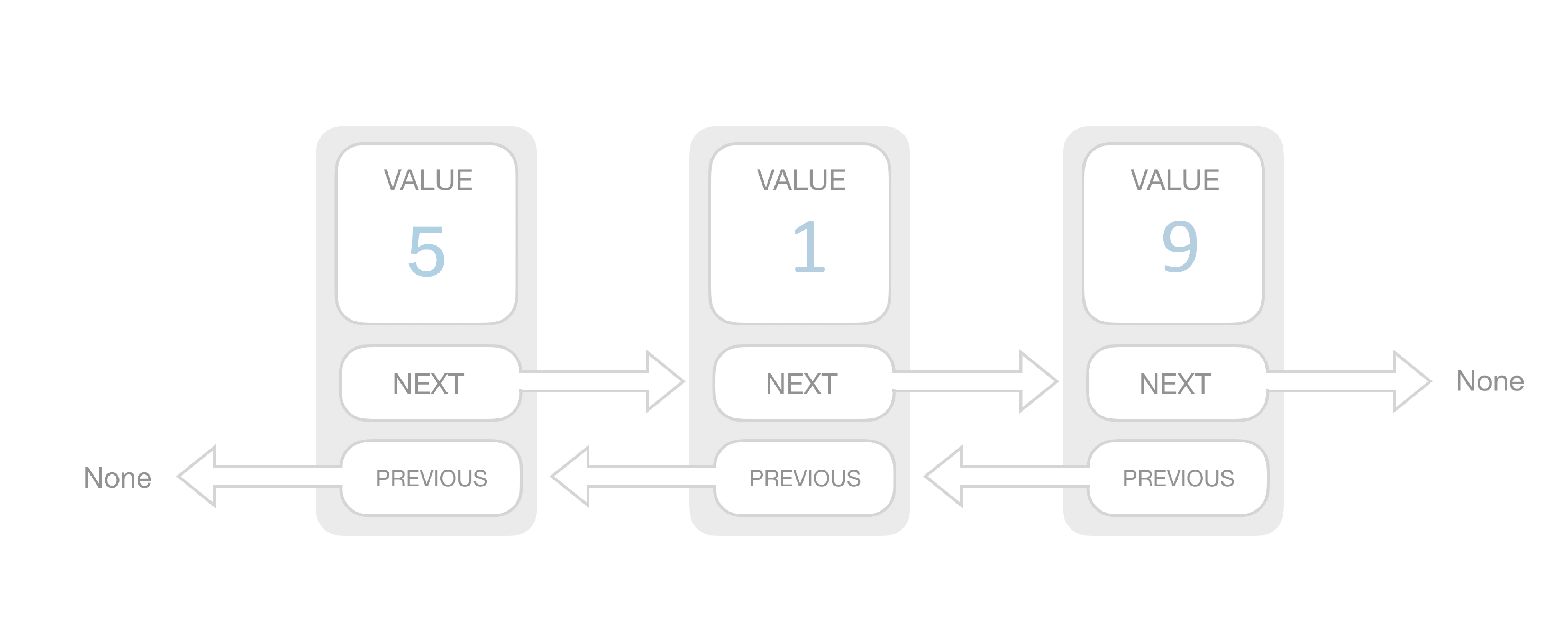
复杂度分析 space: O(n) prepend: O(1) append: O(1) lookup: O(n) insert: O(1) delete: O(1)
Stack & queue
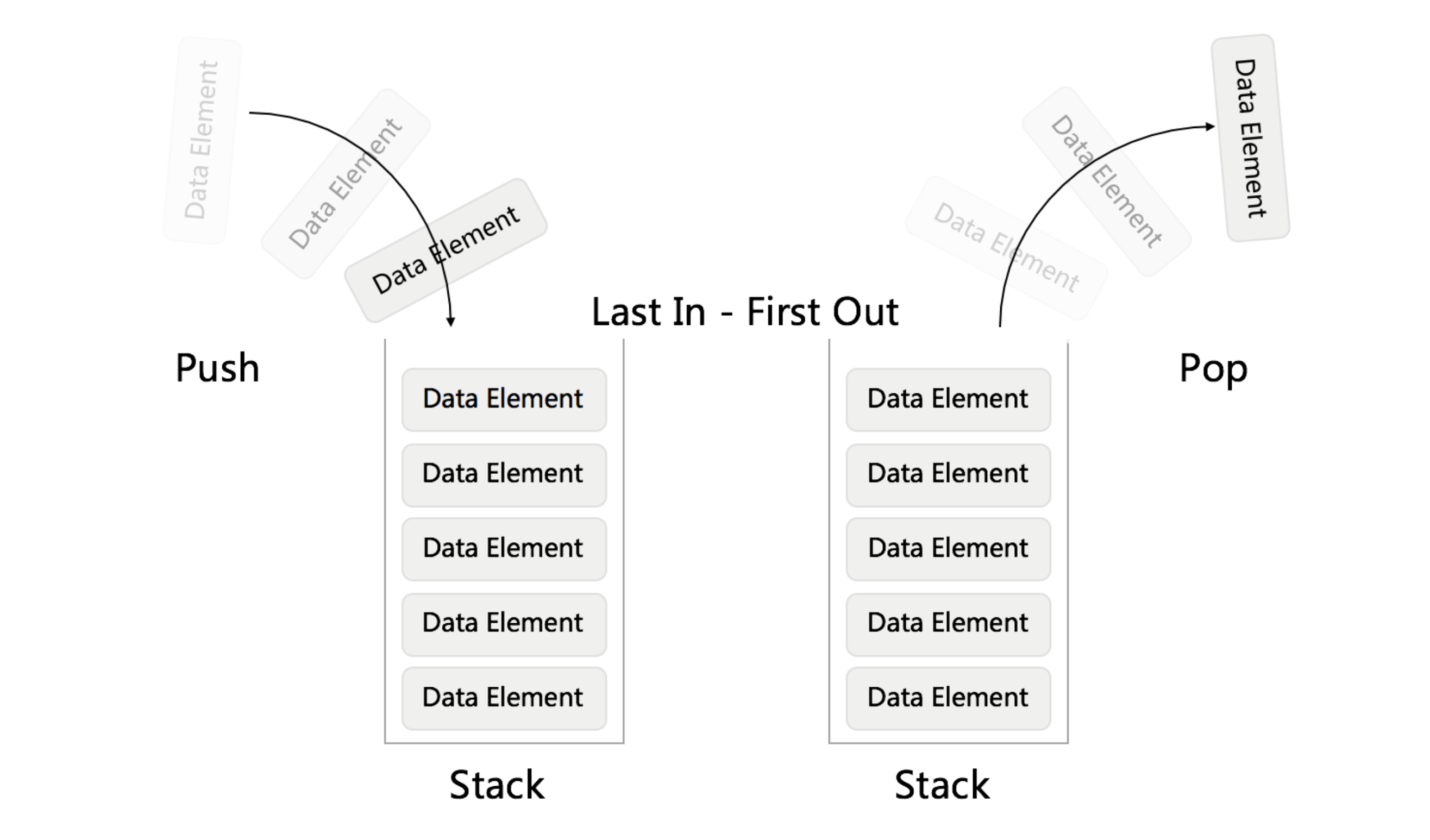
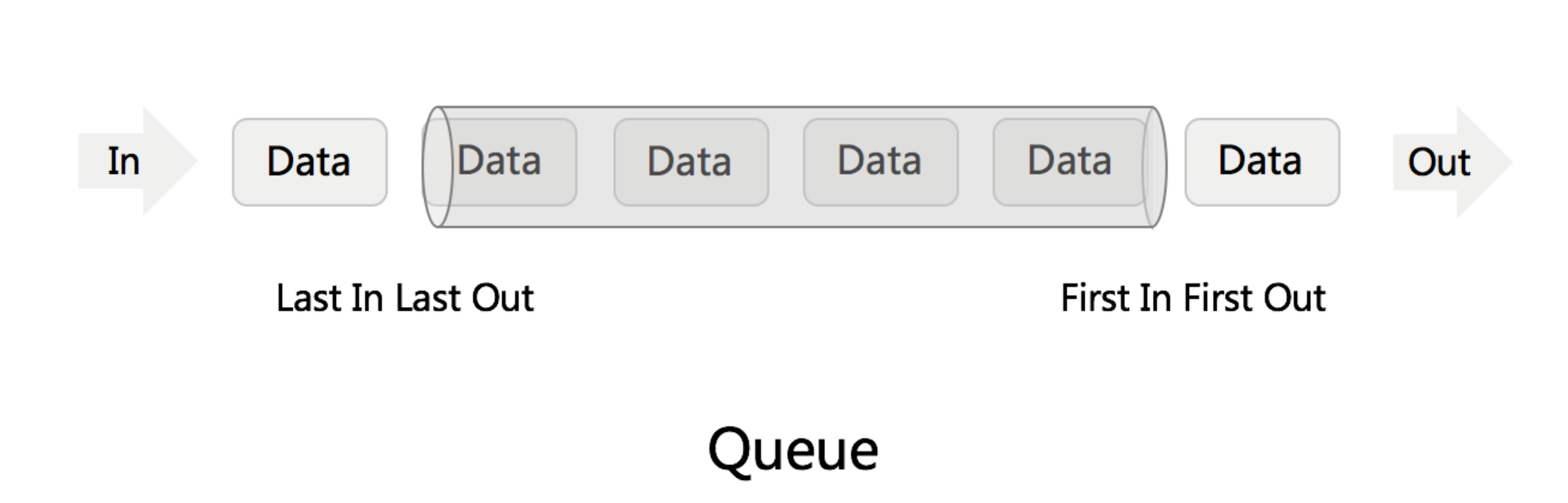
Stack - First In First Out (FIFO) Queue - First In Last Out (FILO)
PriorityQueue
Stack - First In First Out (FIFO) Queue - First In Last Out (FILO) PoriorityQueue - 优先队列
实现机制
- Heap (Binary, Binomial, Fibonacci)
- Binary Search Tree
两种堆
- 小顶堆
- 大顶堆
HashTable & Set
1. Hash Function 2. Hash Collisions
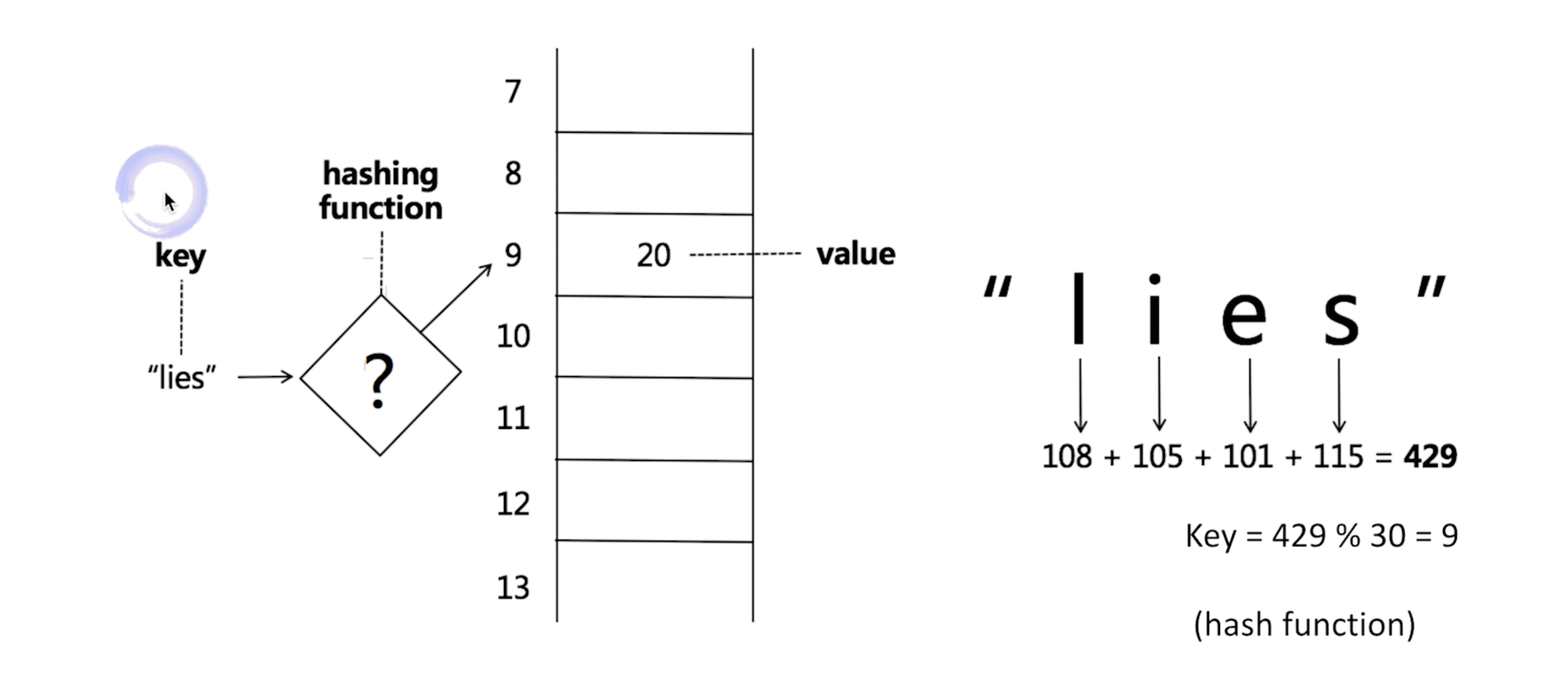
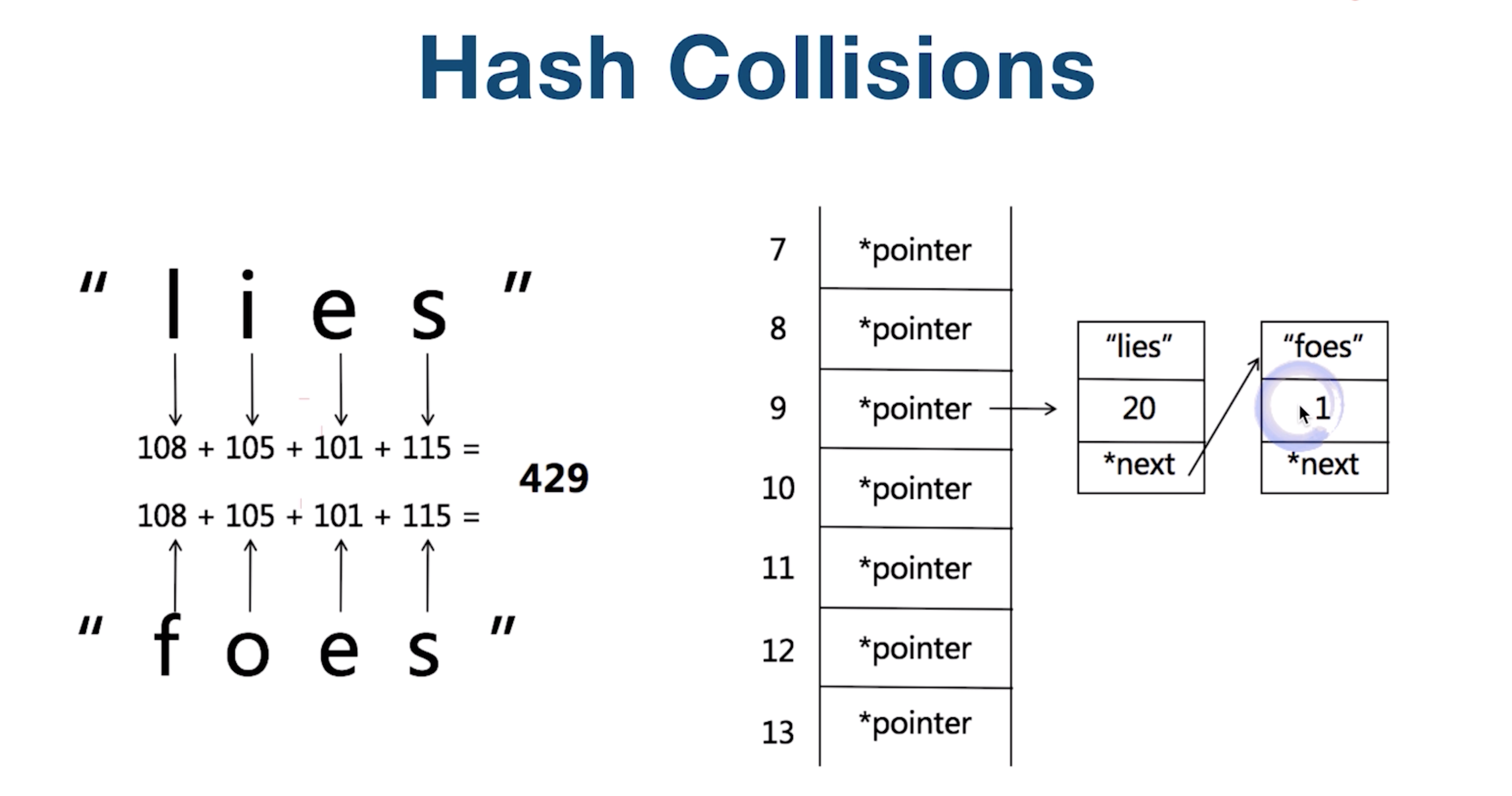
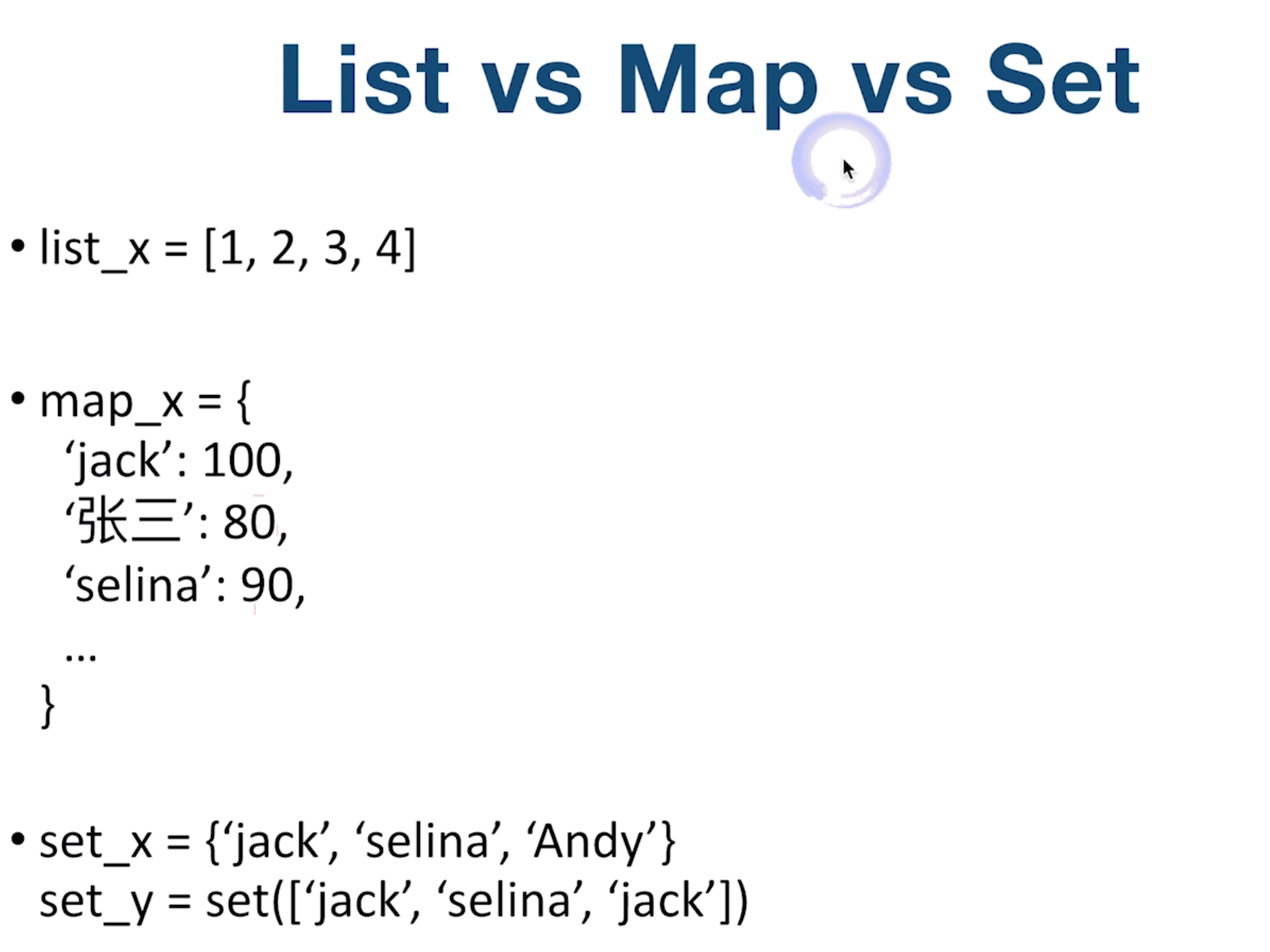
Tree & Binary Tree & Binary Search Tree
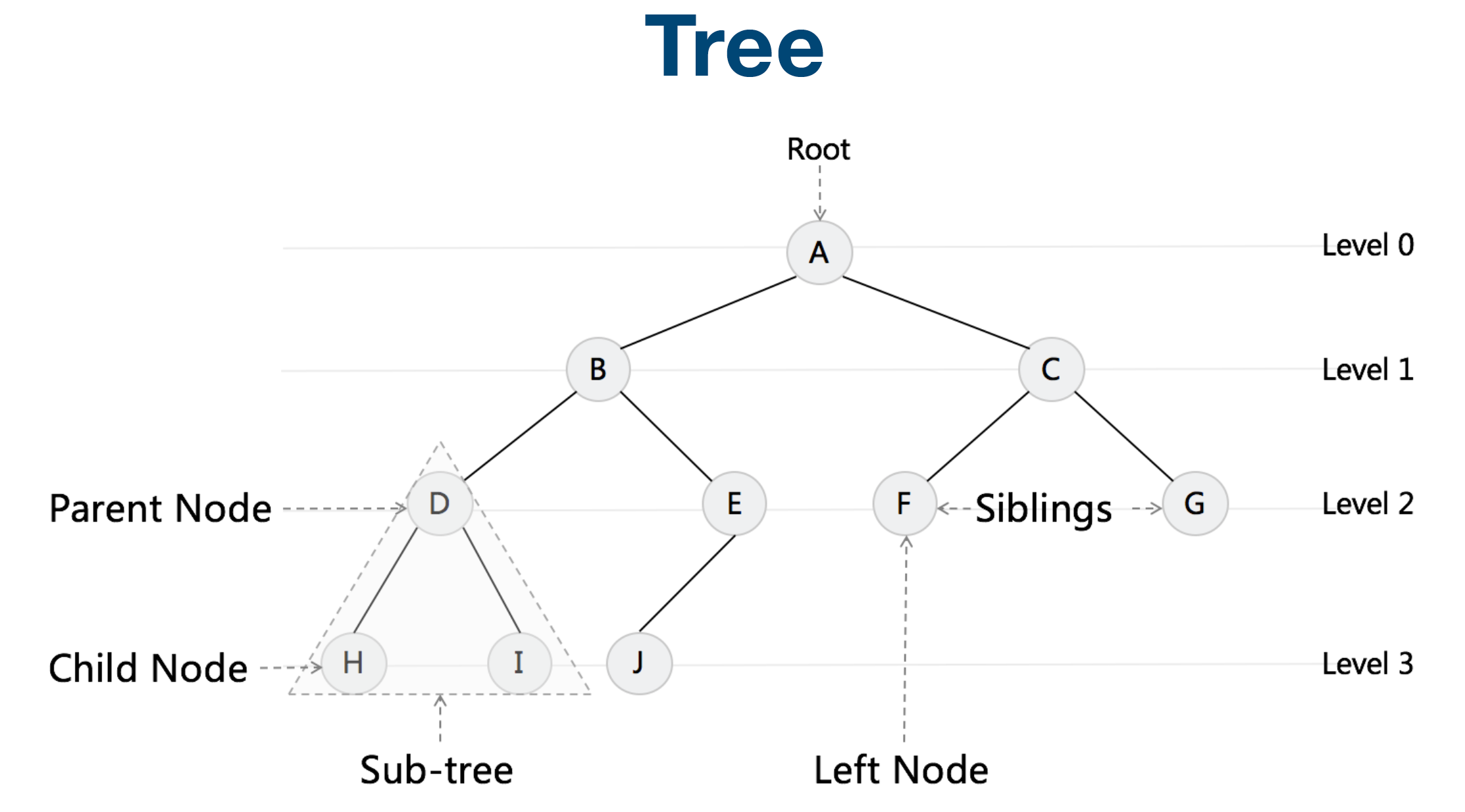
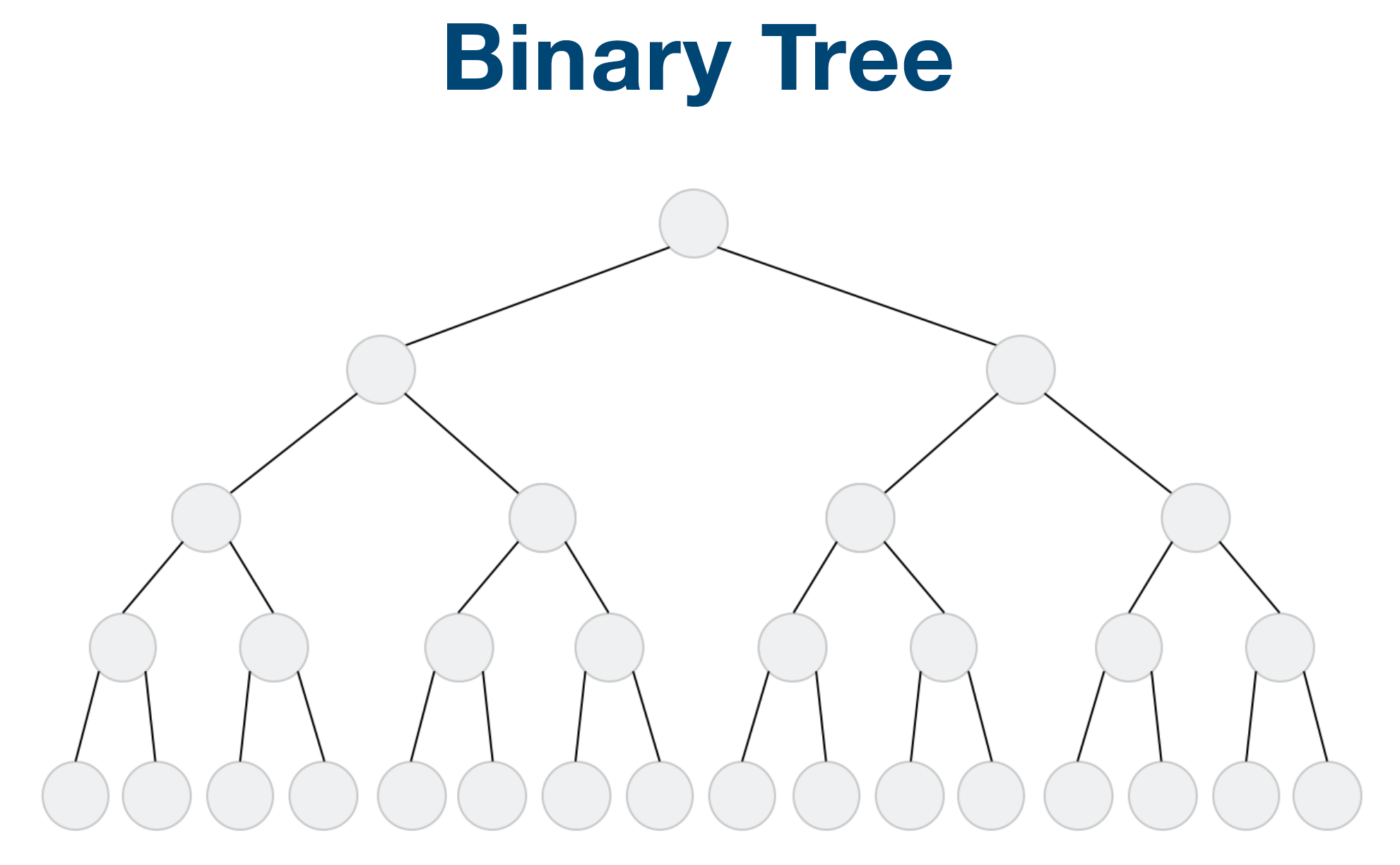
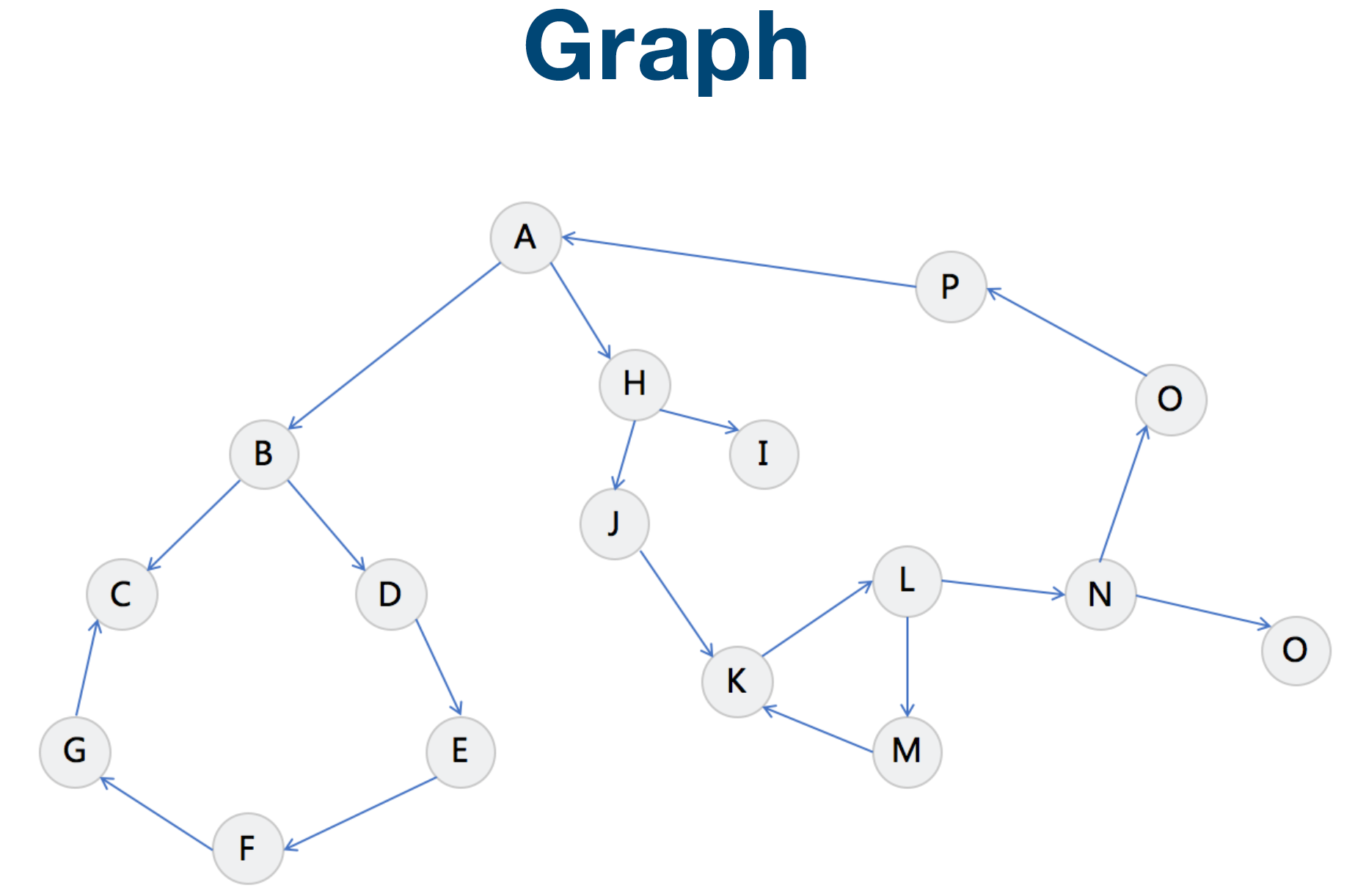
Linked List 就是特殊化的 Tree Tree 就是特殊化的 Graph
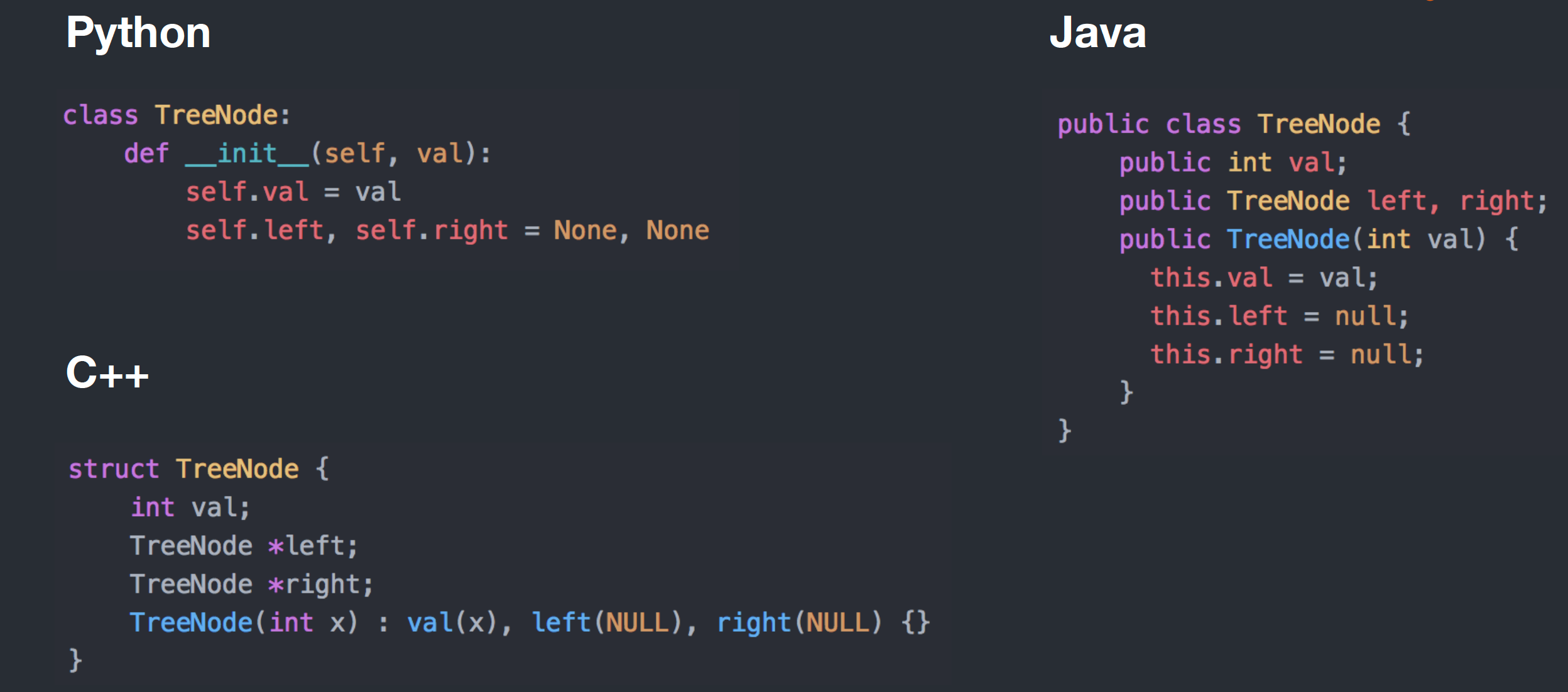

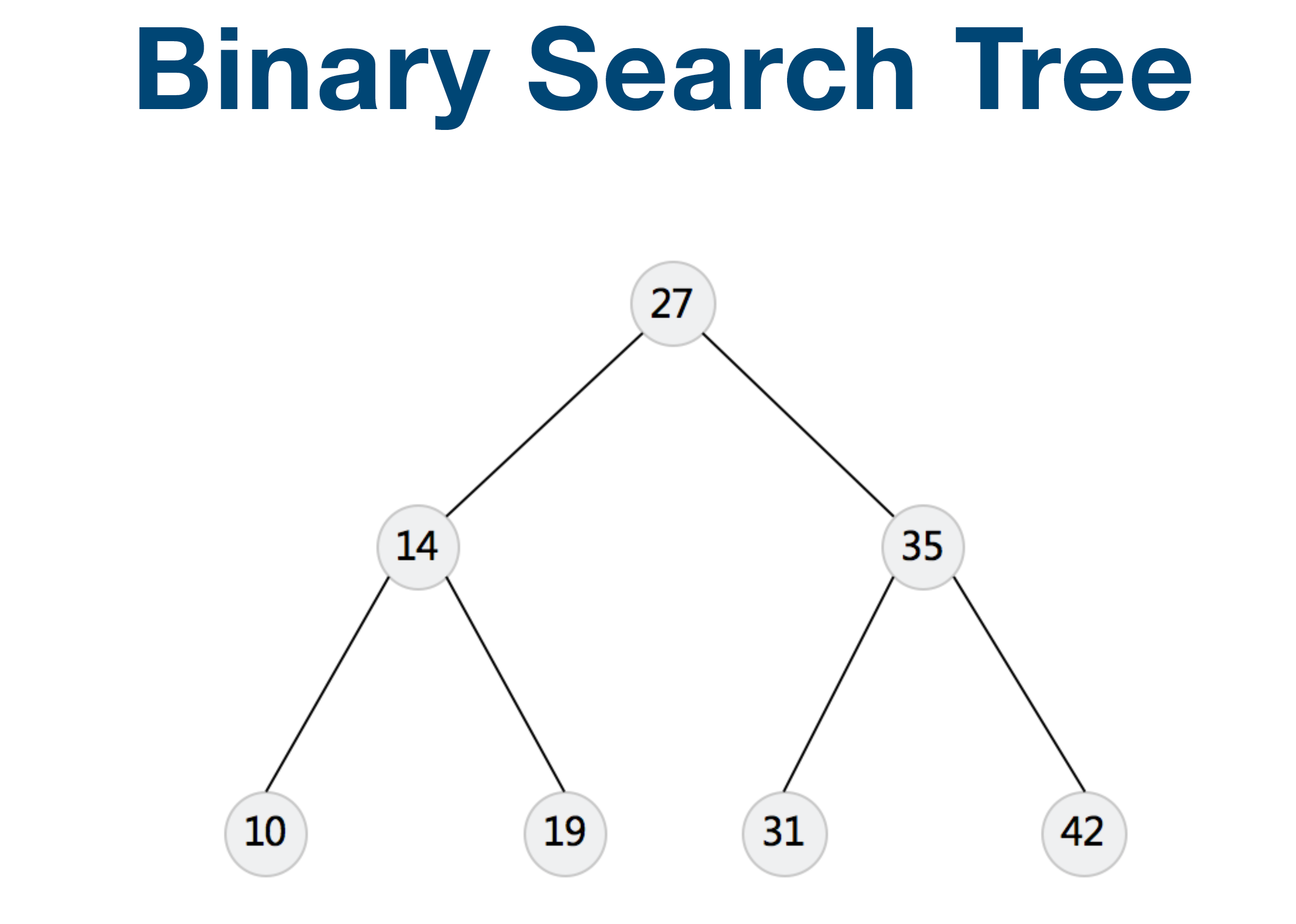
TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
return left == null ? right : right == null ? left : root;
}
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
if p.val < root.val > q.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
if p.val > root.val < q.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
return root
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
while root:
if p.val < root.val > q.val:
root = root.left
elif p.val > root.val < q.val:
root = root.right
else:
return root
二叉树遍历
前序(Pre-order)根-左-右 中序(In-order)左-根-右 后序(Post-order)左-右-根
def preorder(self, root):
if root:
self.traverse_path.append(root.val)
self.preorder(root.left)
self.preorder(root.right)
def inorder(self, root):
if root:
self.inorder(root.left)
self.traverse_path.append(root.val)
self.inorder(root.right)
def postorder(self, root):
if root:
self.postorder(root.left)
self.postorder(root.right)
self.traverse_path.append(root.val)
递归 & 分治
Recursion

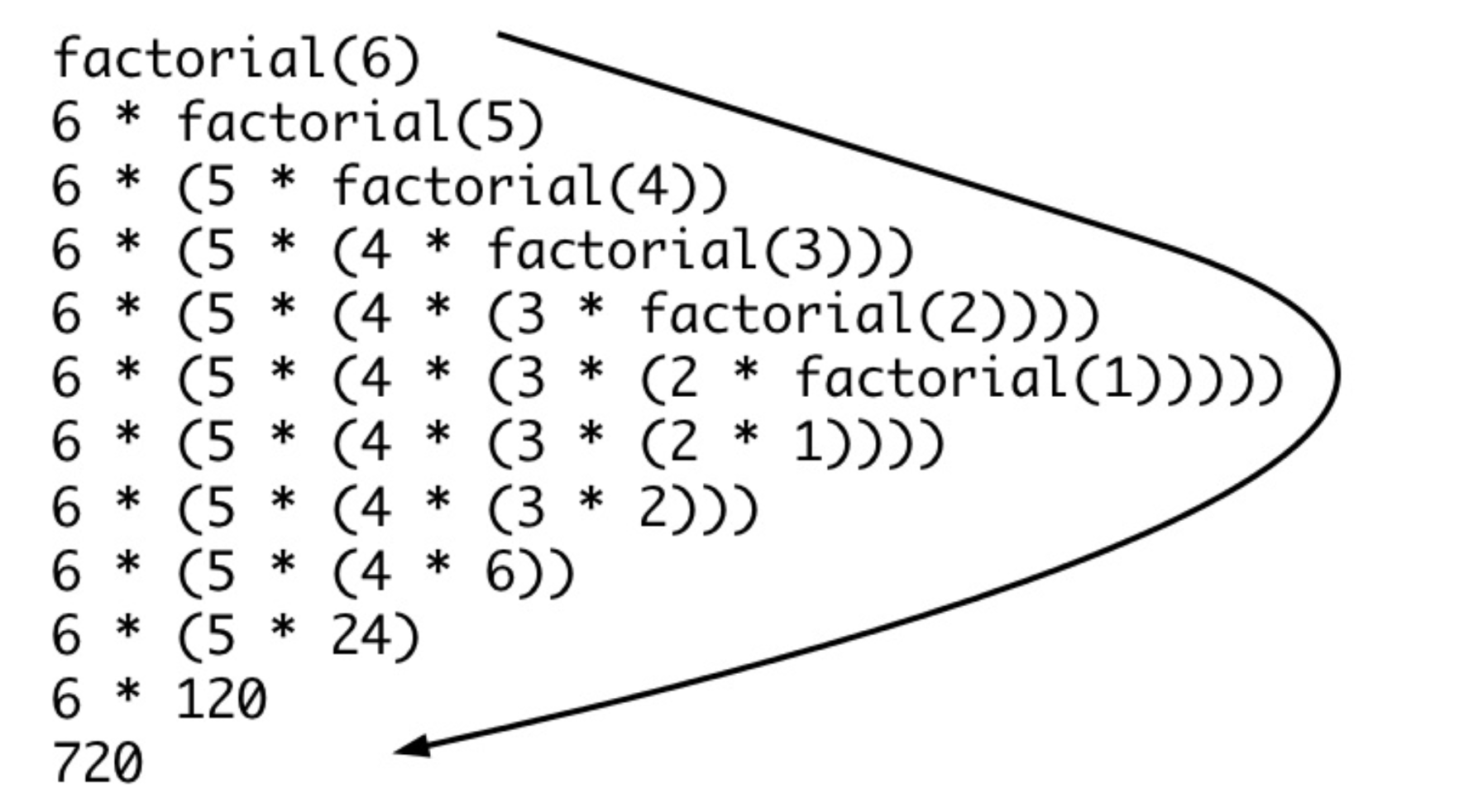

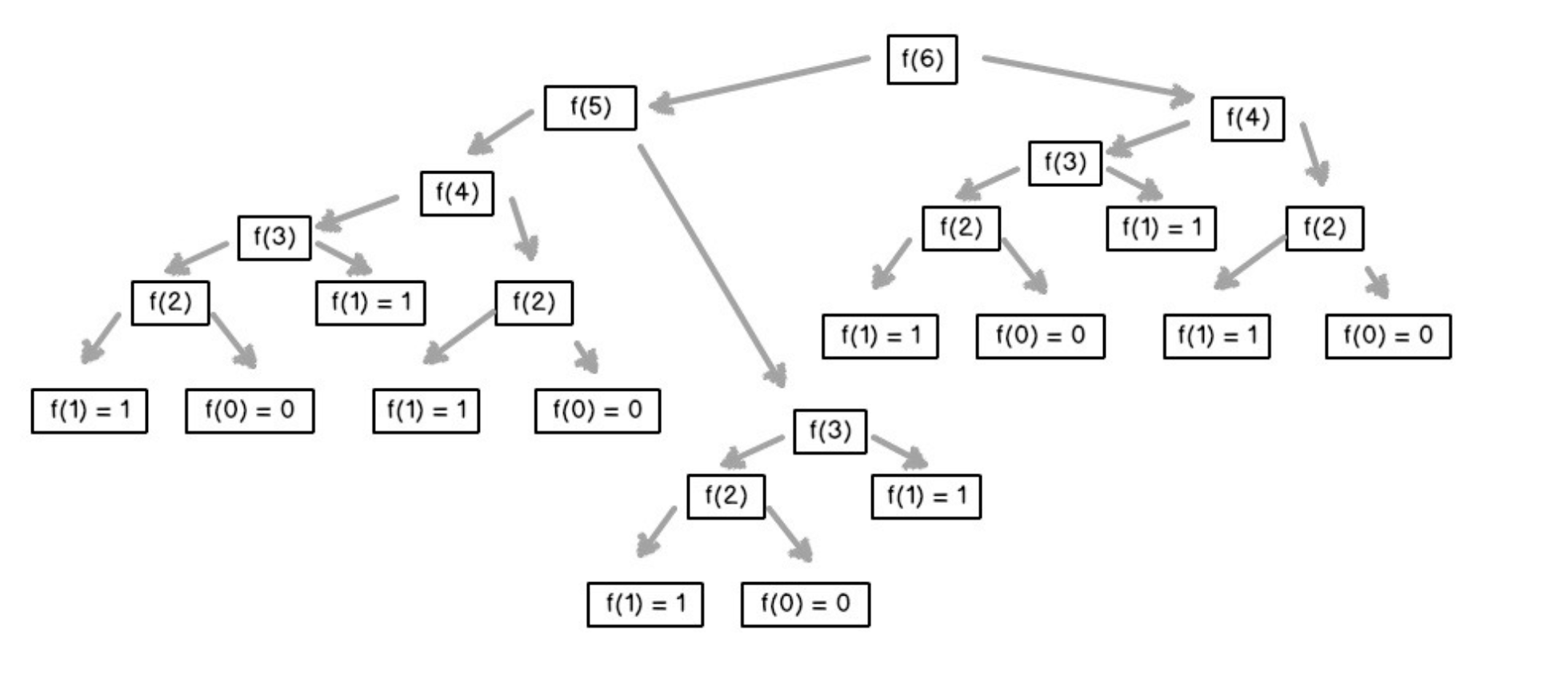
def recursion(level, param1, param2, ...):
# recursion terminator
if level > MAX_LEVEL:
print_result
return
# process logic in current level
pocess_data(level, data...)
# drill down
self.recursion(level + 1, p1, ...)
# reverse the current level status if needed
reverse_state(level)
Divide & Conquer
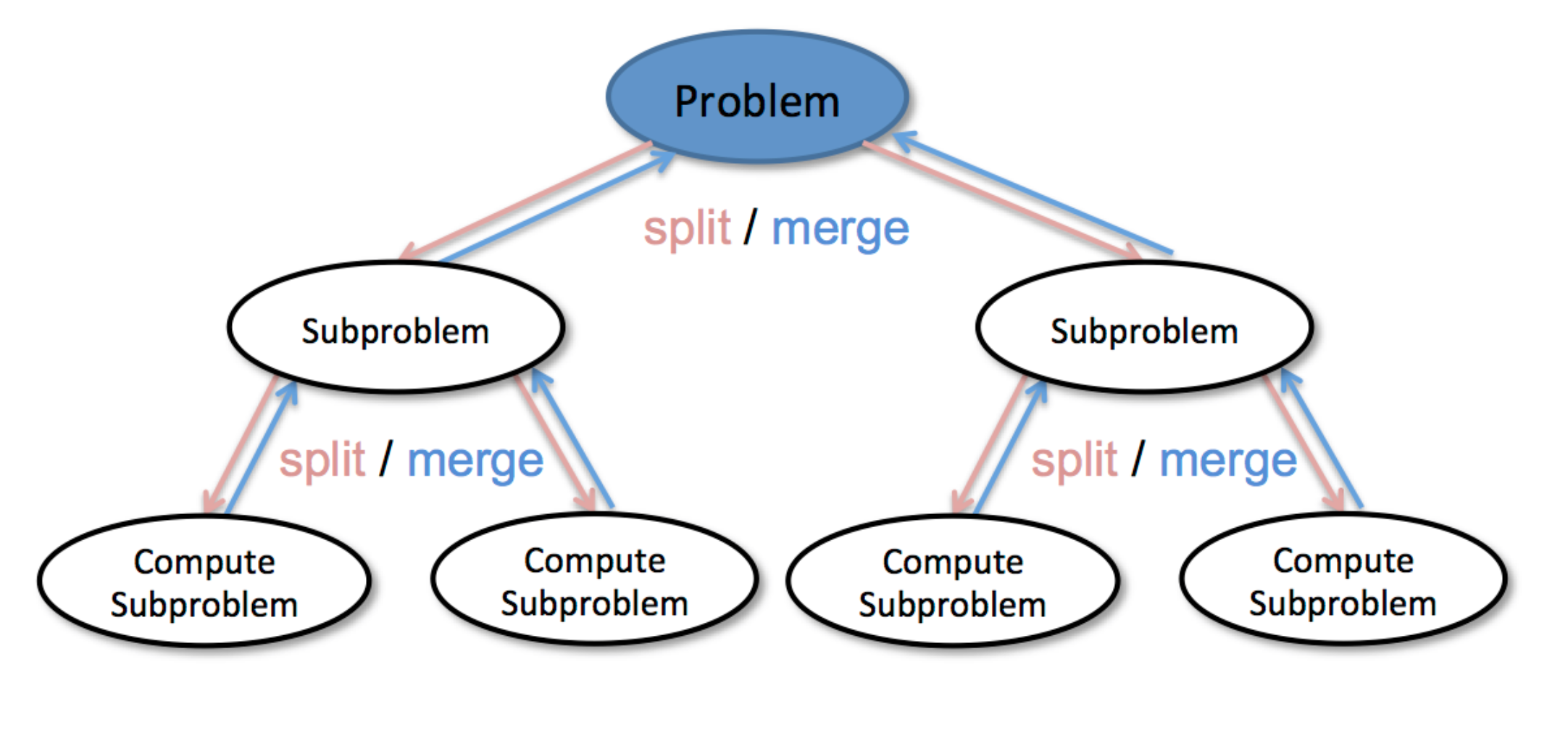
def divide_conquer(problem, param1, param2, ...):
# recursion terminator
if problem is None:
print_result
return
# prepare data
data = prepare_data(problem)
subproblems = split_problem(problem, data)
#conquer subproblems
subresult1 = self.divide_conquer(subproblems[0], p1, ...)
subresult2 = self.divide_conquer(subproblems[1], p1, ...)
subresult3 = self.divide_conquer(subproblems[2], p1, ...)
...
# process and generate the final result
result = process_result(subresult1, subresult2, subresult3, ...)
贪心算法(Greedy Algorithms)

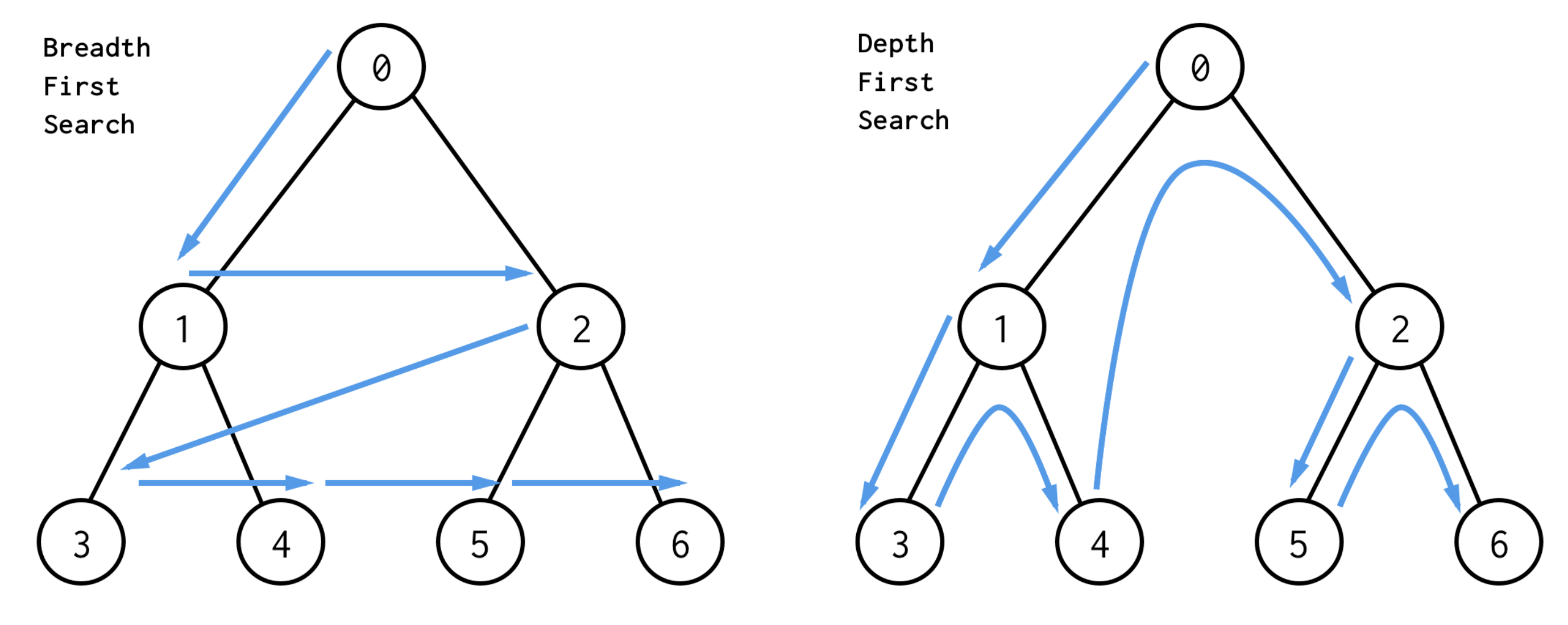
广度优先搜索(Breeadth-First-Search)
How a BFS Would Traverse This Tree
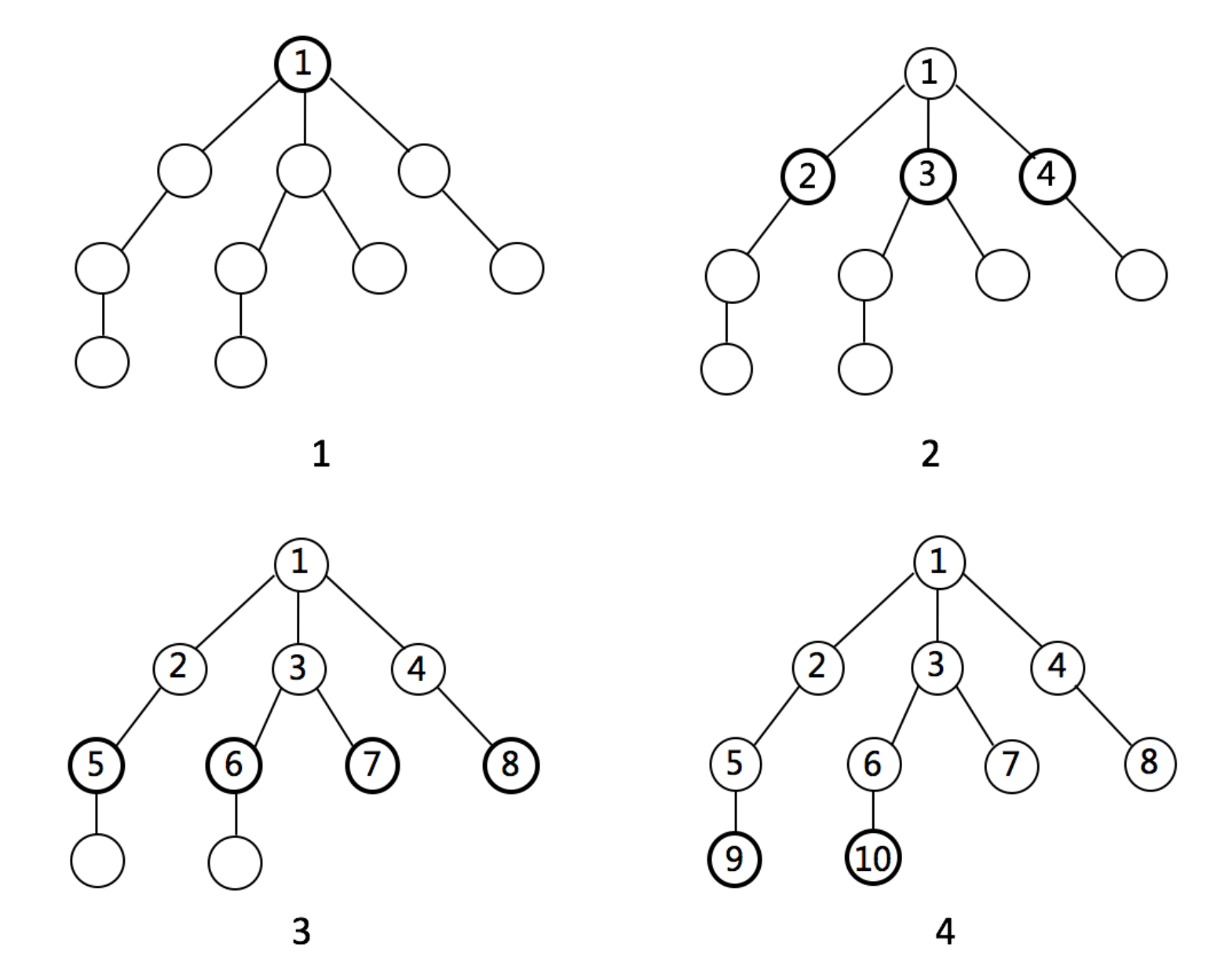
def BFS(graph, start, end)
queue = []
queue.append([start])
visited.add(start)
while queue:
node = queue.pop()
visited.add(node)
process(node)
nodes = generate_related_nodes(node)
queue.push(nodes)
# other processing work
深度优先搜索(Depth-First-Search)
How a DFS Would Traverse This Tree
BFS vs DFS
DFS 递归写法
visited = set()
def dfs(node, visited):
visited.add(node)
# process current node here.
...
for next_node in node.children():
if not next_node in visited:
dfs(next_node, visited)
DFS 非递归写法
def DFS(self, tree):
if tree.root is None:
return []
visited, stack = [], [tree.root]
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
visited.add(node)
process(node)
nodes = generate_related_nodes(node)
stack.push(nodes)
# other processing work
...
二分查找(Binary Search)
Union & Find
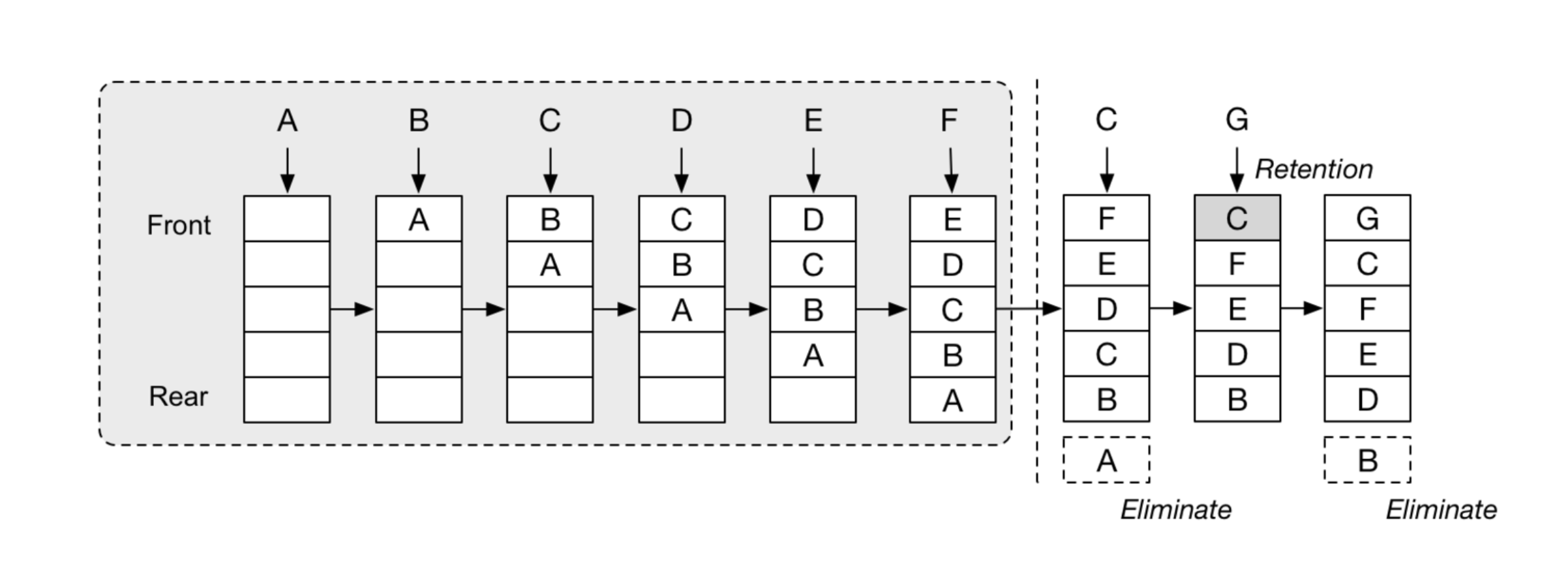
LRU Cache
三个要点:
- Least Recently Used
- Hash Table + Double LinkedList
- O(1) get and O(1) set
常用两种:
- LFU - least frequently used
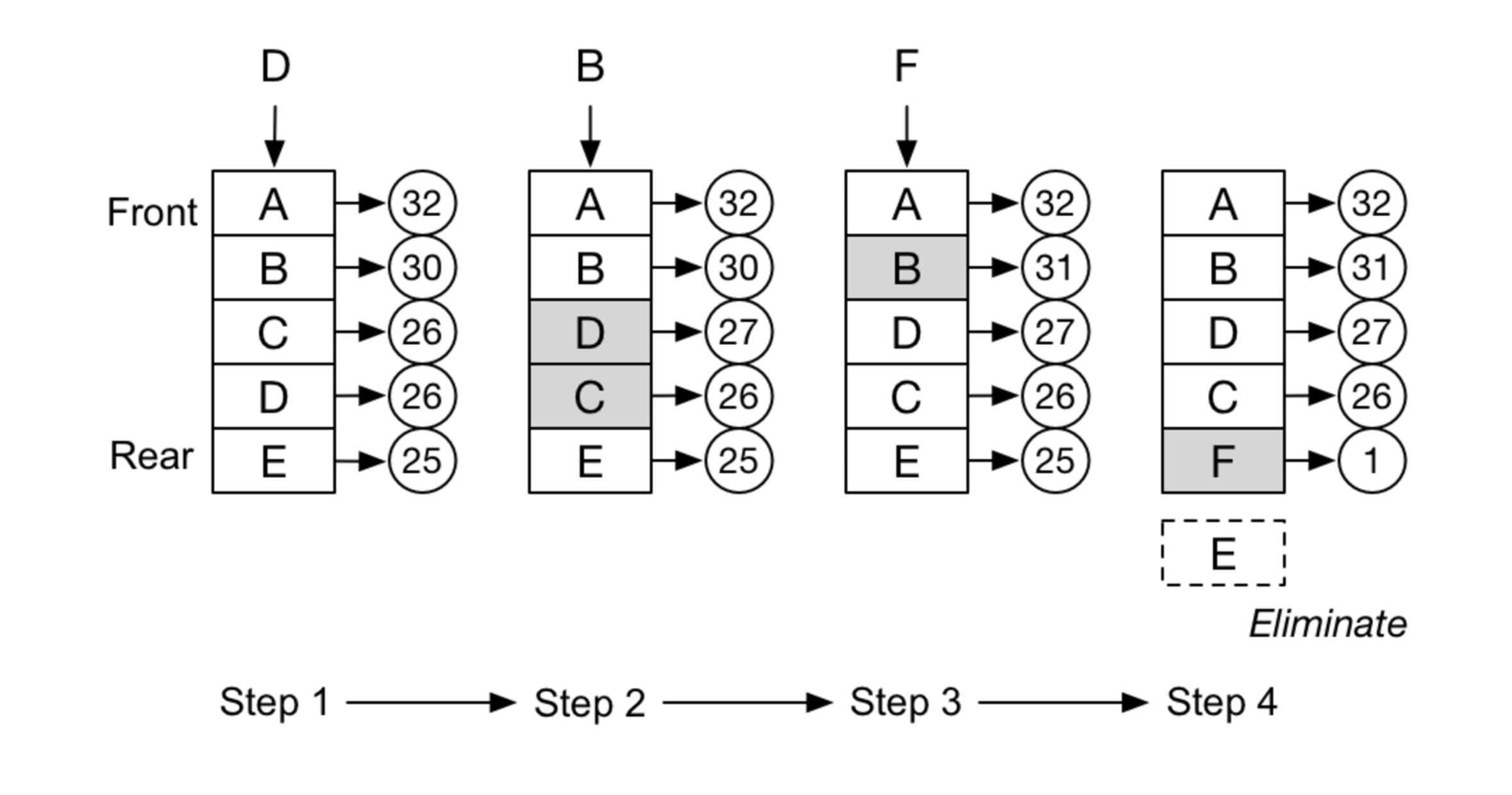
- LRU - least recently used
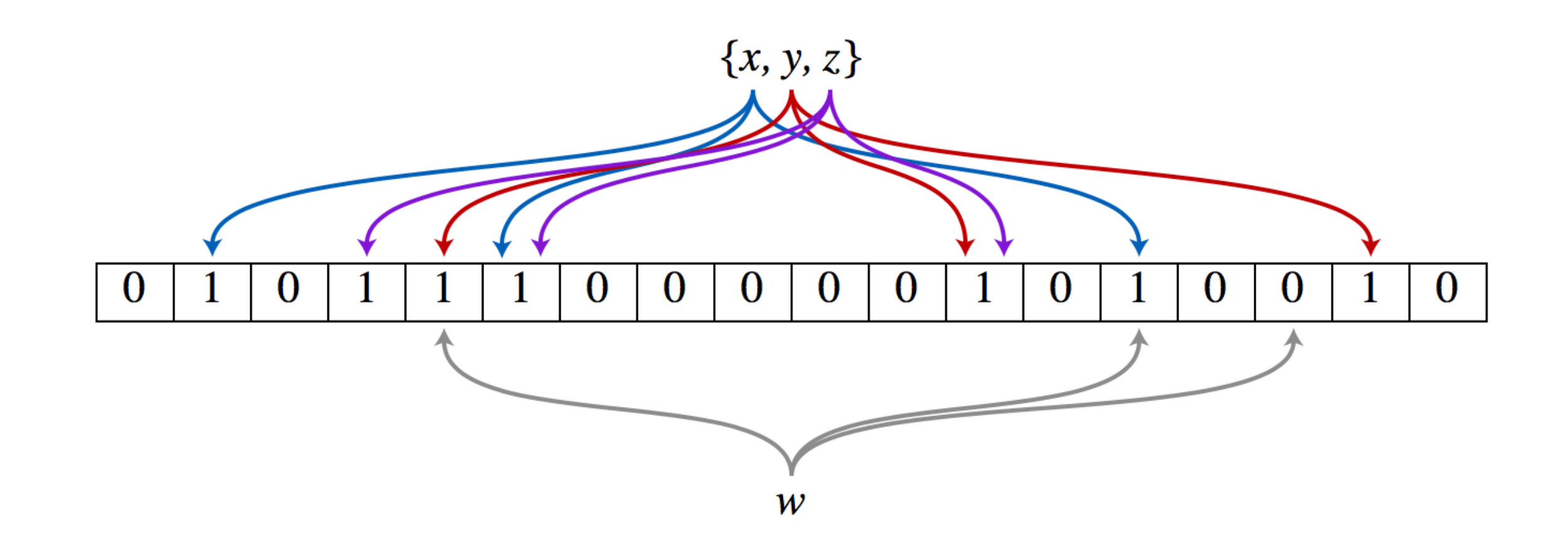
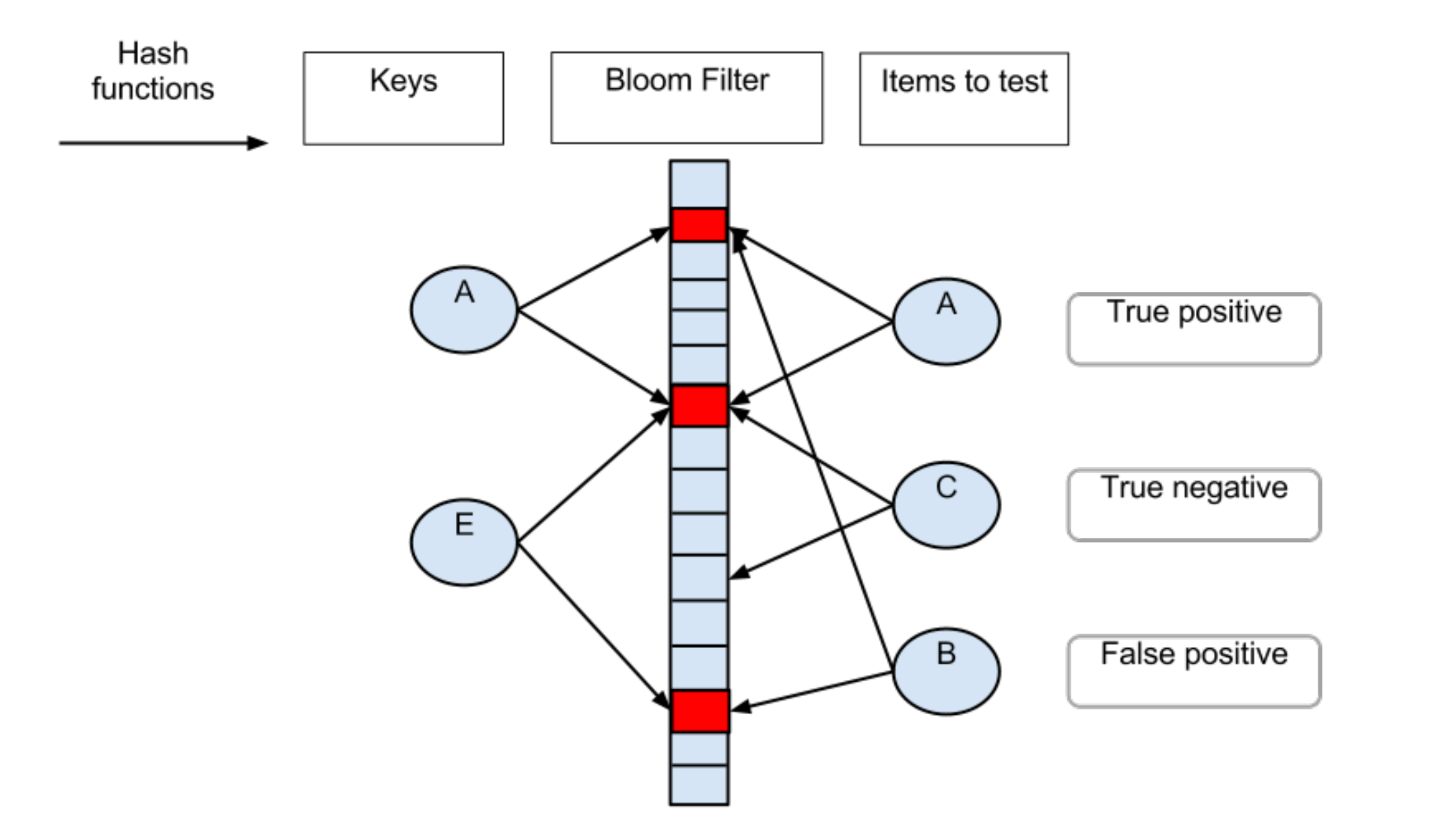
Bloom Filter
两个特点:
- 空间效率和查询速度远超一般算法
- 查询不存在肯定不存在
- 查询存在但不一定存在,需要再次确认
- 查询不存在肯定不存在情况
- 查询存在但不一定存在情况
Comments:
Email questions, comments, and corrections to hi@smartisan.dev.
Submissions may appear publicly on this website, unless requested otherwise in your email.